Immune imaging and therapy – In vivo visualization of presence of immune cells as predictive factor for immune modulating therapies, and exploitation of immune system as therapeutic strategy
In the last decade, immunotherapy has revolutionized the oncology field and has become the standard of care for some cancer types. However, variations in therapy responsiveness and side effects limit the broad applicability and effectiveness of these therapies and highlights the need for both improved immunotherapies and improved screening.
Immune therapy is a cornerstone in our nanobody-based research. In this research pilar we develop and use nanobodies to image important immune cells and key immune activation or inhibitory molecules, as a guide to advance immune therapy efficacy. We employ these nanobodies as diagnostic tracers to follow-up or predict immunotherapy responsiveness by imaging immune cell dynamics, mostly in an oncology context. We also develop nanobody-technologies with immuno-therapeutic activities themselves and take advantage of our knowledge on nanobody-engineering to make the most proficient compounds and methodologies. We also use nanobodies as targeting guides for immune cells, for instance with the development of so-called nanoCAR-T and other kinds of immune cells.
Nanobody clinical translation
Within MITH we generate diagnostic and therapeutic compounds and tracers based on the nanobody-scaffold as a targeting vehicle. The compounds bind to medically-relevant targets and bring either a diagnostic (radioactive or fluorescent) or a therapeutic moiety to the tissue and cells of interest. Hit compounds are first tested in vitro on biophisical aspects and on cells and validated in animal models. Compounds of highest interest and potential are targeted for clinical testing in the university hospital, or together with partners. A clean-room facility is available to ferment nanobodies in single-use bioreactors at gram-scale and subsequent downstream purification using state-of-the-art equipment. We can perform chemical modifications and perform in-house quality testing. This generates GMP- and GLP-grade material for small and smart clinical trials. All the processes are first developed and optimized at low scale in the wet-lab and tested in animal models, and then tech-transferred to the clean-room suite. Radiolabeling occurs with our neighbors of the Brussels Imaging Pharmacy, with whom we share office space and vision. We translate our own preclinically-validated compounds but also partner with academics and provide services for companies.
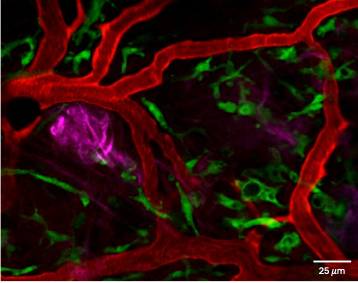
Intravital Imaging
Intravital microscopy (IVM) allows unprecedented 3D spatiotemporal imaging at cellular and subcellular resolution in living animals. Equipped with a Leica Thunder stereomicroscope and a 2-photon Stellaris 8 DIVE microscope, our IVM unit offers simultaneous intravital imaging at meso-and microscale. Embedded within the ICMI Core Facility, we can concurrently perform nuclear and optical imaging at macroscale level. By exploiting our unique setting and longstanding imaging expertise, we facilitate IVM-mediated assessment of drug delivery, therapy responses, vascularity, cellular interactions and regeneration in the context of oncology, immunology, neurobiology, diabetes and more. We further provide assistance with the generation of injectables, their radioisotope or fluorescent labelling, the design and surgical placement of windows, data acquisition and analysis. Just reach out to us so we can help you image the unimaginable!
Nanobody technology – Generation and preclinical validation of novel nanobody-compounds targeting complex cell membrane proteins
Transmembrane proteins, including various receptors, transporters, and channels, play a crucial role in several physiological processes and diseases. As a result, these types of proteins are among the most important targets for drugs. However, the biggest challenge lies in finding (small) molecules that bind to these proteins with high affinity, potency, and selectivity. Nanobodies, antibody fragments derived from camelids, are an ideal therapeutic tool for such proteins. Nanobodies are small, bind to proteins with high affinity and specificity, and can bind epitopes, such as receptor-ligand domains, that are often inaccessible to conventional proteins.
We aim to develop nanobodies against these complex transmembrane proteins for both research and therapeutic purposes. A special focus is placed on developing nanobodies targeting G-protein-coupled receptors. These nanobodies can be reformatted into various formats (multivalent nanobodies, Fc-fusion proteins) and can be used for fundamental research (studying signaling pathways, protein conformations, etc.), diagnostics and/or therapeutic applications (inhibiting receptor activity, targeted therapy).
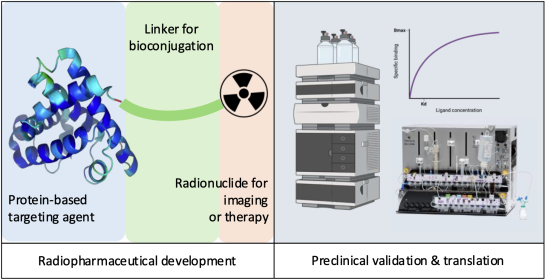
Radiochemistry – Exploration of novel strategies to radiolabel nanobodies and peptides
The Radiochemistry Unit develops radiolabeled proteins for nuclear imaging and therapeutic applications. A key challenge in protein radiolabeling is that they are often sensitive to the harsh conditions required in radiochemistry, risking loss of affinity or degradation by radiolysis. To overcome these issues, we explore novel radionuclides and linker strategies while developing site-specific functionalization methods—both chemically and enzymatically. We ensure the integrity of our radiolabeled products through rigorous quality control, stability assessments, and preclinical studies. Beyond fundamental research, we focus on translation by scaling up radiolabeling methods and implementing automated production protocols using Trasis modules, paving the way for clinical applications.
The radiochemistry unit is open for external researchers, offering access to equipment and expert technical support. Additionally, we provide training opportunities for students and visiting scientists, guiding them through radiolabeling techniques and quality control processes.
Our radioactive lab is fully equipped for radiopharmaceutical development, offering:
- Radio-HPLC systems, Radio-TLC, radio-SDS-PAGE, and Western blot for radiochemical and biochemical analysis, including detection capabilities for gamma and alpha emitters, as well as fluorescent probes.
- Two Trasis All-In-One modules for research and translational applications
- Supporting equipment, including pH meter, centrifuges, heaters, sonicator, and peristaltic pumps.
Our mission is to meet the growing demand for personalized and specialized diagnostic tracers, ultimately enhancing patient care. By developing cutting-edge radiopharmaceutical techniques, we strive to accelerate innovation and reduce the cost of life-saving treatments.